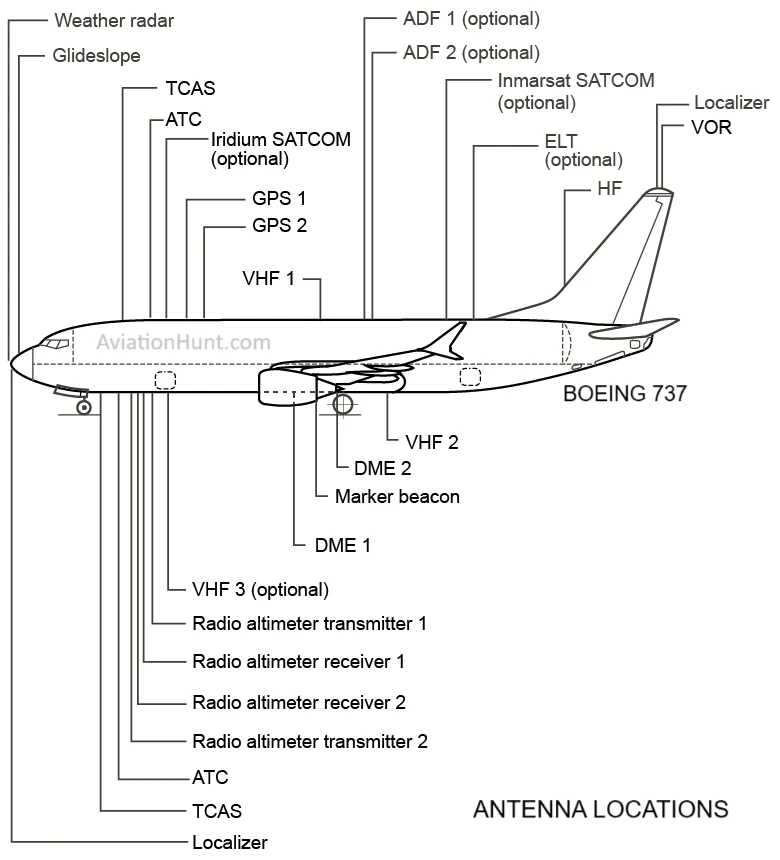

Overview of all antenna locations on a Boeing 737 aircraft –
- Weather Radar: Positioned at the nose of the aircraft, this antenna is used for detecting and monitoring weather conditions ahead, ensuring safe navigation around hazardous weather.
- Glideslope Antenna: Found in the nose section of the aircraft, it provides vertical guidance during approaches and landings as part of the Instrument Landing System (ILS).
- TCAS (Traffic Collision Avoidance System) Antennas: Located on the top and bottom of the fuselage, these antennas enable the system to detect and help avoid potential mid-air collisions by tracking nearby aircraft.
- ATC (Air Traffic Control) Communication Antennas: These are positioned on both the top and bottom of the fuselage for reliable two-way communication with air traffic control.
- Iridium SATCOM (optional): Located on the top of the fuselage, this antenna provides satellite communication capabilities for data and voice communication over long distances.
- GPS Antennas (GPS 1 and GPS 2): Positioned on the top of the fuselage, they provide precise navigation data for flight management systems.
- VHF Communication Antennas:
- VHF 1: Located on the top of the fuselage.
- VHF 2: Positioned on the bottom of the fuselage.
- VHF 3 (optional): Typically found on the top or bottom of the fuselage, used for supplementary communication.
- DME (Distance Measuring Equipment) 1 and 2: Positioned on the bottom of the fuselage, these antennas help determine the distance between the aircraft and ground-based stations for navigation.
- Marker Beacon Antenna: Located on the bottom of the fuselage, this antenna detects signals from ground-based marker beacons to identify specific points during an approach.
- Radio Altimeter Transmitters (1 and 2) and Receivers (1 and 2): Mounted on the bottom of the fuselage, they send and receive signals to measure the aircraft’s altitude above the ground.
- ADF (Automatic Direction Finder) 1 and 2 (optional): Located on the top of the fuselage, these antennas receive signals from non-directional beacons (NDBs) to aid in navigation.
- Inmarsat SATCOM (optional): Also positioned on the top of the fuselage, it supports satellite-based communication for global connectivity.
- ELT (Emergency Locator Transmitter) (optional): Found on the top of the fuselage, this antenna transmits the aircraft’s location during emergencies to assist in search and rescue operations.
- HF (High Frequency) Antenna: Mounted on or integrated into the vertical stabilizer, this antenna facilitates long-range communication, essential for transoceanic flights.
- Localizer Antenna: Typically mounted in the nose section of the aircraft, it provides lateral guidance as part of the ILS during approach. Note: The localizer antenna is not found in the vertical stabilizer; please disregard its placement in the image nomenclature.
- VOR (VHF Omnidirectional Range) Antenna: Found on the vertical stabilizer, this antenna receives signals from VOR ground stations for navigation and enroute guidance.
